Hi, in this post we will disscuss how programmatic ads work. Several platforms of programmatic ads, like Increase rev – collaborate with the client during the online campaign to reach The Highest Possible Income.
Those are Demand-side Platforms which stand by the advertiser side. That possesses the publisher’s inventory and ad exchange. Where they all meet, and data providers like DMP collect, organize and manage audience data.
These platforms, like SSP, DSP, DMP, and Ad Exchange, are part of the complete process. Let’s look at each type to understand clearly:
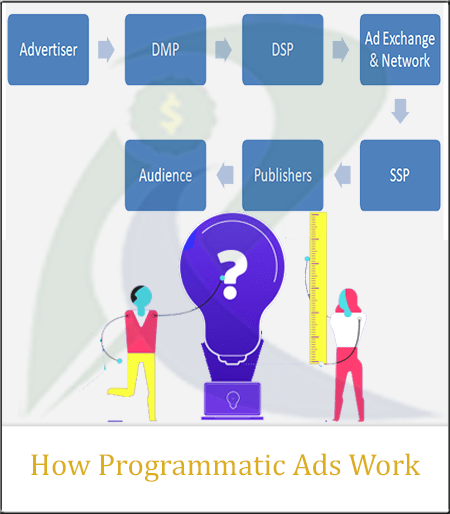
How Programmatic Ads Work
SUPPLY SIDE PLATEFORM:
An SSP holds the publisher’s ad inventory. The publisher submits its webpage as a platform for advertisement. Simply SSP contains a bulk of Ad inventories. Then they sale out these inventories for the relevant and highest ads when we talk about how programmatic ads work.
SSP helps the publisher to increase revenue through their ad inventory. It is allowed publishers to filter the ads by an advertiser. Many of the larger web publishers of the world use a supply-side platform. It helps them to automate and optimize the selling of their online media space.
DEMAND SIDE PLATFORM:
DSP is a programmatic platform designed for advertisers, where advertisers make their bids on DSP. Demand-side platforms make a decision that; when and where the ad will be published – for the best audience response.
Having the bulk of advertisement facilitates DSP to choose the best inventory and negotiate on price.
DATA MANAGEMENT PLATFORM:
A DMP is an independent platform that gathers, oversees, breaks down, and enacts data. The platform gives extensive client profiles to advertisers. The information can be utilized in a programmatic algorithm. It coordinates with the most visitors destined to change to the best advertisement.
AD EXCHANGE:
The ad exchange is a buying and selling platform for DSP and SSP. Or, in other words, it’s a trade of Ad inventory. Ad exchanges enable advertisers to enable advertisers. Publishers to directly sign up for ad exchange or through any advertising agencies. These buying and selling can further be categorized into different types:
REAL-TIME BIDDING:
It is a server-to-server buying process; that allows inventory to be bought and sold in real time. Real-time bidding takes place exactly at the time when a user visits the website.
HEADER BIDDING:
The advanced bidding mechanism, where publishers offer ad inventory to various pre-defined ad exchanges set up by ad providers like Increase Rev. Header bidding advertisers to bid for Ad inventory and run a bid between ad exchanges. They bid for an ad inventory in the last only the highest bidder wins.
It can quickly increase the publisher’s revenue while giving all exchanges an equal shot at higher-quality placements.
EXCHANGE BIDDING:
This is a server-side unified auction. According to Google’s exchange introduction, bidding allows other exchanges and SSPs to compete with Google Ad Exchange in a unified auction.
OPEN AUCTION:
An Open Auction publisher’s inventory is available for all advertisers/ad agencies. Any advertiser/ad agency can bid on open auction inventories through specific targeting. Publishers offer their specific minimum amount for ad inventory, and advertisers within the ad exchange bid on inventories. The highest bid wins the inventory. Open bidding is for everyone.
PRIVATE MARKETPLACE:
Buying and selling between only a few advertisers and sellers. It also follows Real Time Bidding. But in PMPs, the publisher has more control over the advertisement advertised on their page or website.
FIRST PRICE AUCTION:
In a first-price auction, all programmatic buyers will contend in one sale, close by the direct-sold advertiser. In the first price auction – the winner has to pay the exact price for what he bid. No matter how less the runner-up will pay.
SECOND PRICE AUCTION:
The runner-up will set the price for the impression where the winner will only have to pay a cent more than the runner-up. This encourages the advertisers to bid the highest amount possible.
PREFERRED DEAL:
Preferred Deal is a feature that allows sellers to offer inventory. It can provide inventory to a single advertiser through multiple buyers. Some publishers also choose to offer certain inventory exclusively by preferred deals. They gain access to the inventory by bidding at or above the negotiated fixed price.
IMPORTANCE OF PROGRAMMATIC ADS FOR PUBLISHERS:
Programmatic ads make publishers more protected by hosting ads relevant to their content. This tech does not bother the user and increases the stay time on the publishers’ page. Publishers can also increase revenue with different bidding deals, as mentioned above.
Programmatic ads help publishers by making it easier to sell the ad inventory. The relevancy of ads helps publishers to grow efficiently.
IMPORTANCE OF PROGRAMMATIC ADS FOR ADVERTISERS:
Initially, 60% of the ad inventory went unsold, and sold inventory was not much affective as expected by advertisers. It Creates communication problems. Programmatic advertisement has solved those issues and makes it easy to buy ad inventories.
Advertisers could not identify whether their ads were reaching out to the actual audience or not. Programmatic Ad technology offers a layer of transparency; that wasn’t available in traditional advertisement. Whereas it also gives real-time analytics to the advertiser.
